

Asking whether there is an ideal BMI for women is the same as asking whether there is an ideal BMI for men. These indicates that there is no ideal BMI range for a gender category or even particularly for age ranges. Of late, there has been a consensus in the medical fraternity that the BMI cut off for Asian populations should be 23 since these populations have been found to be more vulnerable to diabetes. All you need here is common sense to know that if a person with a height of 4 feet has a BMI equal to that of a 6-feet individual, the shorter person’s BMI is clearly not ideal. These figures apply across the board irrespective of ages as well. Anything above 30 is categorised as obese. Broadly speaking, irrespective of whether you are male or female, a BMI in the range of 18.5 to 24.9 is considered normal. The ideal BMI varies from person to person depending not only on height and weight but other factors too. Body mass index is thus basically an indicator of how much fat one’s body has depending on that person’s height and weight. Knowing what your BMI or body mass index is a good way to find out whether you are obese or underweight. If you are feeling sluggish or lacking energy, chances are that you have too much fat for your height and weight or comparatively less fat than what is recommended. Being overweight can lead to a host of health problems. Thin people can have high levels of visceral fat, even though they might be considered healthy by BMI standards, but they may pose a higher risk of developing health problems related to weight gain.Ĭurrently without a viable way to change how we measure body fat, BMI is still the best option. Visceral fat is more harmful that fat that is stored just under the skin. It’s located near several vital organs, including the liver, stomach, and intestines. For instance, Visceral fat is a type of body fat that’s stored within the abdominal cavity also known as Belly fat. Muscle tends to be heavier and can move more toned individuals into the overweight status, even if their fat levels are low.īMI also doesn’t tease apart different types of fat, each of which can have different metabolic effects on health. Scientists have said that BMI cannot distinguish between fat and muscle. Below are the target goals for waist circumference measurements. Sometimes even when your BMI is within healthy range, having too much fat around the abdomen (apple-shaped body) will still put you at risk for heart disease and diabetes. *BMI may not apply to athletes who tend to have large muscle mass, elderly people, pregnant women and children. Risk of nutritional deficiency diseases and osteoporosis. 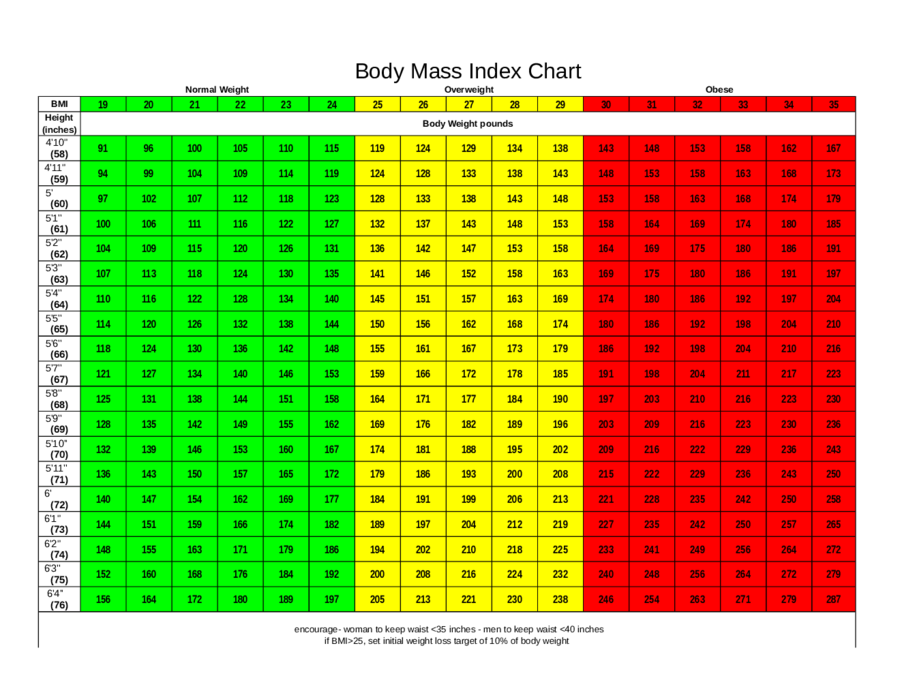
Low risk: Continue exercising and eating healthfully.
ADULT BMI CALCULATOR HOW TO
Talk to your healthcare provider about your ideal body weight and how to make healthy lifestyle changes. Moderate Risk: Your risk for developing type 2 diabetes and other chronic diseases are higher. It increases the risk for developing many chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes, and decreases overall quality of life. High Risk: Your weight is further above healthy range. Rather than an emphasis on weight, the BMI cut-offs are presented with an emphasis on health risk in the table below. In Singapore, the BMI cut-off figures were revised in 2005, after studies have shown that Singaporeans including many Asian populations, have higher proportion of body fat and increased risk for cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus as compared with general BMI recommendations in other countries. BMI Categories (WHO):īMI Calculator Asian (Singapore) vs BMI Calculator Western However, because at any given BMI, Asians, including Singaporeans, generally have a higher percentage of body fat than do Caucasians, the BMI cut- off levels for Singaporeans have been revised such that a BMI 23 kg/m2 or higher marks a moderate increase in risk while a BMI 27.5 kg/m2 or more represents high risk for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.īMIs under 20.0 and over 25.0 have been associated with higher all-cause mortality, increasing risk from the 20.0–25.0 range. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines overweight as a BMI of ≥ 25 and a BMI of ≥ 30 for obesity. It is defined as a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of his height in meters (kg/m2). The body mass index (BMI) is a simple and the most commonly used index used to classify overweight and obesity. Calculation: x 10,000 (round to one decimal place)Įxample: Lily’s weight is 32.5 kg and her height is 109.2 cm.You can calculate your BMI manually using the metric system:






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
